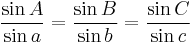Abū al-Wafā' Būzjānī
| Full name | Abu al-Wafa' al-Buzjani |
|---|---|
| Born | June 10, 940 Buzhgan |
| Died | 997 or 998 CE Baghdad |
| Era | Islamic Golden Age |
| Region | Islamic civilization |
| Main interests | Mathematics and Astronomy |
| Notable ideas | |
| Major works | Almagest of Abū al-Wafā' |
|
Influenced by
|
|
|
Influenced
|
|
Abū al-Wafāʾ, Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Ismāʿīl ibn al-ʿAbbās al-Būzjānī[1] (10 June 940 – 15 July 998) was a Persian[2] mathematician and astronomer who worked in Baghdad. He made important innovations in spherical trigonometry, and his work on arithmetics for businessmen contains the first instance of using negative numbers in a medieval Islamic text.
He is also credited of compiling tables of sines and tangents at 15' intervals. He also introduced the sec and cosec and studied the interrelations between the six trigonometric lines associated with an arc.[3] His Almagest was widely read by medieval Arabic astronomers in the centuries after his death. He is known to have written several other books that have not survived.
Contents |
Life
He was born in Buzhgan, (now Torbat-e Jam) in Khorasan (in today's Iran). At age 19, in 959 AD, he moved to Baghdad and remained there for the next forty years, and died there in 998.[3] He was a contemporary of the distinguished scientists Al-Quhi and Al-Sijzi who were in Baghdad at the time and others like Abu Nasr ibn Iraq, Abu-Mahmud Khojandi, Kushyar ibn Labban and Al-Biruni.[4] In Baghdad, he received patronage by members of the Buyid court.[5]
Astronomy
Abu Al-Wafa' was the first to build a wall quadrant to observe the sky.[4] It has been suggested that he was influenced by the works of Al-Battani as the latter describes a quadrant instrument in his Kitāb az-Zīj.[4] His use of tangent helped to solve problems involving right-angled spherical triangles, and developed a new technique to calculate sine tables, allowing him to construct more accurate tables than his predecessors.[5]
In 997, he participated in an experiment to determine the difference in local time between his location and that of al-Biruni (who was living in Kath, now a part of Uzbekistan). The result was very close to present-day calculations, showing a difference of approximately 1 hour between the two longitudes. Abu al-Wafa is also known to have worked with al-Kuhi, who was a famous maker of astronomical instruments.[5] While what is extant from his works lacks theoretical innovation, his observational data were using by many later astronomers, including al-Biruni's.[5]
Almagest
Among his works on astronomy, only the first seven treatises of his Almagest (Kitāb al-Majisṭī) are now extant.[6] The work covers numerous topics in the fields of plane and spherical trigonometry, planetary theory, and solutions to determine the direction of Qibla.[4][5]
Mathematics
He established several trigonometric identities such as sin(a ± b) in their modern form, where the Ancient Greek mathematicians had expressed the equivalent identities in terms of chords.[7]
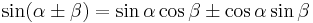
He also discovered the law of sines for spherical triangles:
where A, B, C are the sides and a, b, c are the opposing angles.[7]
Some sources suggest that he introduced the tangent function, although other sources give the credit for this innovation to al-Marwazi.[7]
Works
- Almagest (Kitāb al-Majisṭī).
- "A Book on Those Geometric Constructions Which Are Necessary for a Craftsman", (Kitāb fī mā yaḥtaj ilayh al-ṣāniʿ min al-aʿmāl al-handasiyya).[8]
- "A Book on What Is Necessary from the Science of Arithmetic for Scribes and Businessmen", (Kitāb fī mā yaḥtaj ilayh al-kuttāb wa’l-ʿummāl min ʾilm al-ḥisāb).[8] This is the first book where negative numbers have been used in the medieval Islamic texts.[5]
He also wrote translations and commentaries on the algebraic works of Diophantus, al-Khwārizmī, and Euclid's Elements.[5]
Legacy
The crater Abul Wáfa on the Moon is named after him.
Notes
- ^ "بوزجانی". Encyclopaediaislamica.com. http://www.encyclopaediaislamica.com/madkhal2.php?sid=2053. Retrieved 2009-08-30.
- ^ "Iran" in USECO History of Humanity, ed. by M.A. Bakhit, Volume 4 of History of humanity : scientific and cultural development,UNESCO, 2000 pg 375: ""The science of trigonometry as known today was established by Islamic mathematicians. One of the most important of these was the Persian Abu'l Wafa Buzjani (d. 997 or 998), who wrote a work called the Almagest dealing mostly with trigonometry"" [1]
- ^ a b O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Mohammad Abu'l-Wafa Al-Buzjani", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Abu'l-Wafa.html.
- ^ a b c d Moussa, Ali (2011). "Mathematical Methods in Abū al-Wafāʾ's Almagest and the Qibla Determinations". Arabic Sciences and Philosophy (Cambridge University Press) 21 (1). doi:10.1017/S095742391000007X.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Hashemipour 2007.
- ^ Kennedy, E. S. (1956). Survey of Islamic Astronomical Tables. American Philosophical Society. p. 12.
- ^ a b c Jacques Sesiano, "Islamic mathematics", p. 157, in Selin, Helaine; D'Ambrosio, Ubiratan (2000), Mathematics Across Cultures: The History of Non-western Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 1-4020-0260-2
- ^ a b Youschkevitch 1970.
References
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Mohammad Abu'l-Wafa Al-Buzjani", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Abu'l-Wafa.html.
- Hashemipour, Behnaz (2007). "Būzjānī: Abū al‐Wafāʾ Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ibn Yaḥyā al‐Būzjānī". In Thomas Hockey et al. The Biographical Encyclopedia of Astronomers. New York: Springer. pp. 188–9. ISBN 9780387310220. http://islamsci.mcgill.ca/RASI/BEA/Buzjani_BEA.htm. (PDF version)
- Youschkevitch, A.P. (1970). "Abū’l-Wafāʾ Al-Būzjānī, Muḥammad Ibn Muḥammad Ibn Yaḥyā Ibn Ismāʿīl Ibn Al-ʿAbbās". Dictionary of Scientific Biography. 1. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 39–43. ISBN 0684101149. http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1G2-2830900031.html.
External links
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||